When an Economy Faces Diminishing Returns
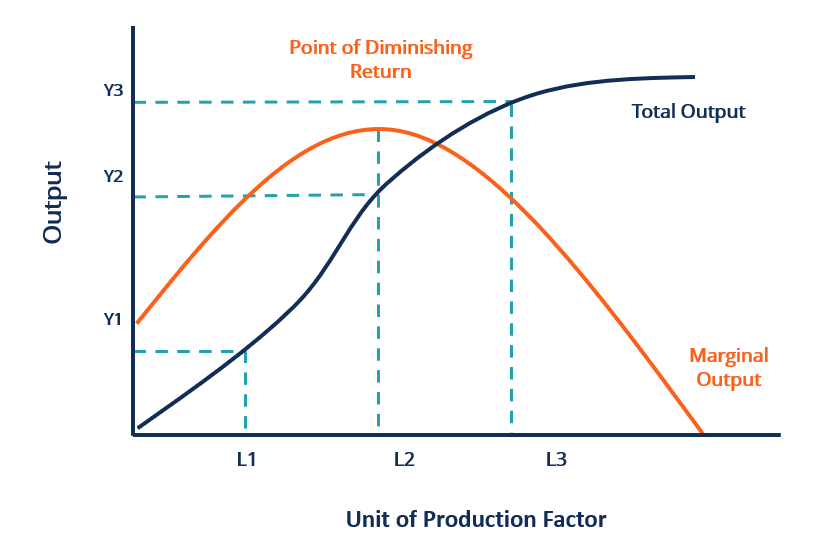
Diminishing Returns occur when one factor of production is held constant while the other factors of production are expanded. This is phenomenon is known as the Law of Diminishing Returns and its key economists understanding of supply and demand as well as how.
Law Of Diminishing Returns Point Of Diminishing Returns Definition
B the per-worker production function shifts to the left.
. When you put in continued effort the returns start to slow down. Because When an economy faces diminishing returns the slope of the per worker production functi. The per-worker production function shifts down.
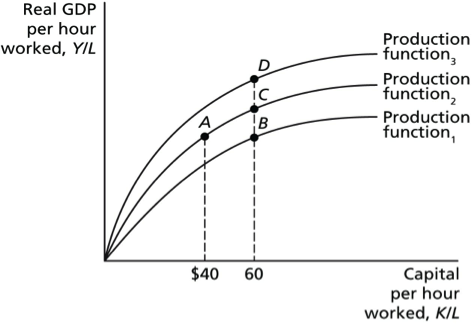
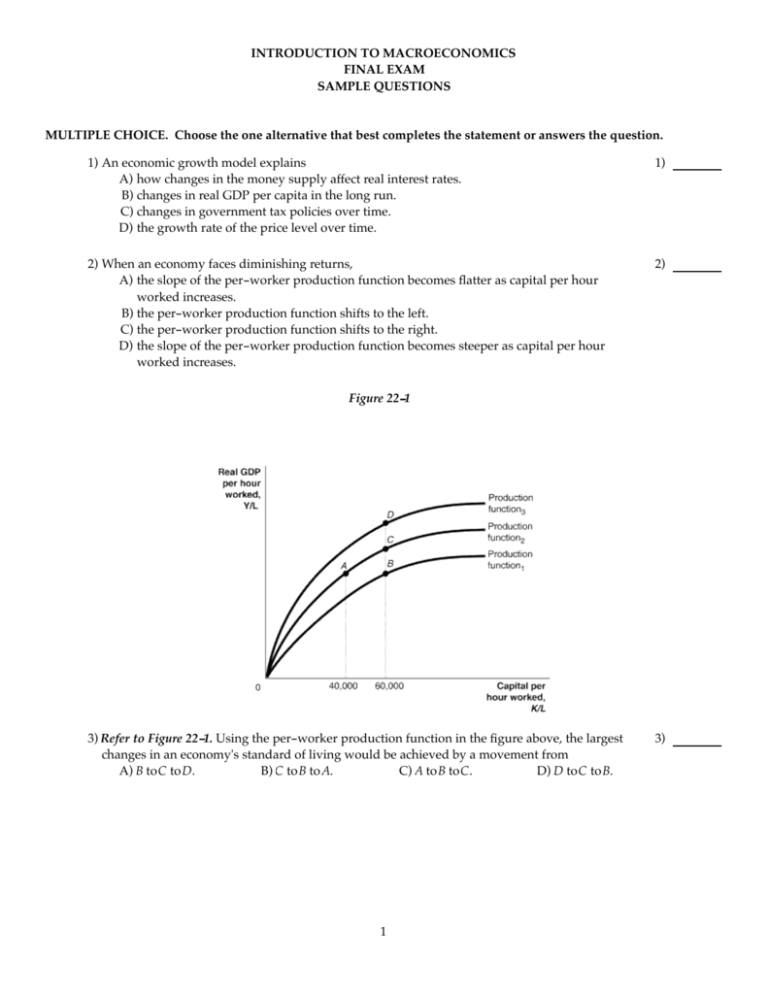
The slope of the per-worker production function becomes steeper as capital per hour worked increases. Answer- 3 Diminishing marginal returns is illustrated in the per-worker production function in the figure above by a movement from point A to point C. The slope of the per-worker production function becomes steeper as capital per hour worked increases.
The per-worker production function shifts to the left. Three main geographical contexts in which similar transport investments can have different multiplying effects are identified. The slope of the per-worker production function becomes steeper as capital per hour worked increases B.
High multiplying effects A. When an economy faces diminishing returns to capital a. 7 When an economy faces diminishing returns A the slope of the per-worker production function becomes steeper as capital per hour worked increases.
The law of diminishing marginal productivity is an economic principle usually considered by managers in productivity management. In reality however there are limits to how much your business will benefit from this method. C the slope of the per-worker production function becomes flatter as capital per hour worked increases.
In other words the total output initially increases with an increase in variable input at given quantity of fixed. B the slope of the per-worker production function becomes flatter as capital per hour worked increases. Generally it states that advantages gained from slight improvement.
When an economy faces diminishing returns. Advantages in economic activities subject to Diminishing Returns with their population rising. In fact in some cases an increase in manpower or machinery can actually lead to a decrease in production.
The law of diminishing marginal utility that we introduced in the last section is a more specific case of the law of diminishing returns When government spends a certain amount more on reducing crime for example the original gains in reducing crime could be relatively large. For example switching from a 10-mile-per-gallon mpg vehicle to a 15-mpg vehicle saves more fuel and results in greater fuel cost savings than. An imbalance in resource utilization is the cause.
In a context where there is. The slope of the per-worker production function becomes flatter as capital per hour worked increases. Increasing the money supply may boost a recessionary economy but it also faces diminishing returns and.
When an economy faces diminishing returns A. The law of diminishing marginal returns states that there comes a point when an additional factor of production results in a lessening of output or impact. The per-worker production function shifts up.
Fuel costs which depend on vehicle fuel economy miles driven and fuel price are an important factor in vehicle purchasing decisions. A the slope of the per-worker production function becomes flatter as capital per hour worked increases. An increase in any individual factor of production may cause diminishing marginal returns if the levels of other factors remain steady.
However fuel economy improvement exhibits diminishing returns in fuel savings. In economics its known as the law of diminishing returns the shrinking benefit you get when you pour ever-increasing resources toward achieving a singular goal. Law of diminishing returns explains that when more and more units of a variable input are employed on a given quantity of fixed inputs the total output may initially increase at increasing rate and then at a constant rate but it will eventually increase at diminishing rates.
Economists consider it a short-term issue however because companies generally are able to make up for the imbalance in time. Select an answer and submit. Diminishing returns once again rears its ugly head.
If the economy faces diminishing marginal returns what will happen to the opportunity cost as the production of one of the categories of goods increases. The per-worker production function shifts to the right. Results occur in 3 phases namely increasing return diminishing return and negative return.
When an economy faces diminishing returns. The initial effort translates to a steep increase in results. A the slope of the per-worker production function becomes steeper as capital per hour worked increases.
The per-worker production function shifts to the right C. When an economy faces diminishing returns A. The per-worker production function shifts to the left.
C the per-worker production function shifts to the left. As you progress further you will hit a point where putting in more effort no longer makes sense. A common fallacy in understanding and assessing the economic impacts of transport investments is the lack of consideration of the diminishing returns these investments can face.
An economy is on its production possibilities frontier. Lowering interest rates is the first and foremost monetary policy tool used by central bankers to boost spending and growth in an.

The Production Function Boundless Economics
Solved I Need To Explain Each Part Of The Question For How I Chegg Com
No comments for "When an Economy Faces Diminishing Returns"
Post a Comment